Article
Solidarity
In May 1983 British Columbians voted the Social Credit Party, headed by William BENNETT, into office. Two months later, on July 7, the Socreds introduced their so-called Restraint Budget, accompanied by 26 prospective bills.

Enter your search term
Signing up enhances your TCE experience with the ability to save items to your personal reading list, and access the interactive map.
Create AccountArticle
In May 1983 British Columbians voted the Social Credit Party, headed by William BENNETT, into office. Two months later, on July 7, the Socreds introduced their so-called Restraint Budget, accompanied by 26 prospective bills.
"https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9

Article
Under Canada’s constitutional monarchy, the sovereign is head of state, the legal foundation of the executive branch of government and one part of Parliament — along with the Senate and House of Commons. The current sovereign of Canada is King Charles III. The sovereign is represented in Canada by the governor general, lieutenant-governors and territorial commissioners and acts on the advice of the prime minister, the head of government.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/KingCharlesIII.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/KingCharlesIII.jpg

Article
Sovereignty is an abstract legal concept. It also has political, social and economic implications. In strictly legal terms, sovereignty describes the power of a state to govern itself and its subjects. In this sense, sovereignty is the highest source of the law. With Confederation and the passage of the British North America Act, 1867, Canada’s Parliament was still legally under the authority of the British Parliament. By 1949, Canada had become fully sovereign in relation to Great Britain. This was due to landmark legislation such as the Statute of Westminster (1931). The Constitution Act, 1982 swept away Britain’s leftover authority. Questions of sovereignty have also been raised by Indigenous peoples in Canada and by separatists in Quebec. The latter, for a time, championed the concept of sovereignty-association.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/39b78f3a-b1bb-47ec-aa0b-d4f5de005157.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/39b78f3a-b1bb-47ec-aa0b-d4f5de005157.jpg

Article
Between 1838 and 1841, Lower Canada was governed by an “authoritarian” political body known as the Special Council.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/9b102db4-f93d-44c3-a26e-d61b3ea11b50.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/9b102db4-f93d-44c3-a26e-d61b3ea11b50.jpg

Article
The Speech from the Throne declares a government’s agenda for a new session of the legislature. The speech contains comments on the state of the country or province and outlines the matters on which the government will seek action. The monarch or their representative — the governor general federally and the lieutenant-governor provincially — delivers the speech; but it is entirely the work of the Cabinet ministers.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/11551bec-a5f6-4e78-b101-265ddf7610cb.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/11551bec-a5f6-4e78-b101-265ddf7610cb.jpg

Article
After a razor-thin majority voted in the 1995 Quebec Referendum for Quebec to stay in Canada, the Liberal government of Prime Minister Jean Chrétien responded with various initiatives to promote federalism in the province. A sponsorship program began in 1996. Public money was directed from the Department of Public Works and Government Services to private advertising agencies to promote Canada and the federal government at cultural, community and sports events in Quebec. The media began questioning the spending and handling of these contracts. Two auditor general reports and a public inquiry revealed that ad agency executives and Liberal Party officials had corruptly handled more than $300 million; $100 million of which was funnelled from the government to the Liberal Party. Five people were found guilty of fraud. Along with several other issues, the scandal helped lead to the government of Chrétien’s successor, Paul Martin, being reduced to a minority in 2004.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/3ec8aa06-d88a-40e2-826e-ed91385b8006.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/3ec8aa06-d88a-40e2-826e-ed91385b8006.jpg

Article
StateThe state is a broad concept that includes government as the seat of legitimate authority in a territory but also includes bureaucracy, judiciary, the ARMED FORCES and internal POLICE, structures of legislative assemblies and administration, public corporations, regulatory boards, and ideological apparatuses such as the education establishment and publicly owned media. The distinguishing characteristic of the state is its monopoly over the use of force in a given territory. The state as a concept in...
"https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9

Article
The first European expeditions that came to Canada to explore and trade for furs did not include women.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/be832524-f521-4200-b242-3c702ae0f3c4.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/be832524-f521-4200-b242-3c702ae0f3c4.jpg

Editorial
The following article is an editorial written by The Canadian Encyclopedia staff. Editorials are not usually updated. In the fall of 1929, Canada’s Minister of Justice, Ernest Lapointe, travelled to England. He took with him Dr. Oscar Skelton — the “elder statesman” of the Canadian civil service, as William Lyon Mackenzie King once described him. When Lapointe and Skelton were done their negotiations, they had confirmed that Canada would have its independence from the British Empire.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/43cb3921-bb9b-4a07-818d-0f1dfeb80b26.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/43cb3921-bb9b-4a07-818d-0f1dfeb80b26.jpg

Article
Stornoway is the official residence of Canada’s federal leader of the Opposition. It is located at 541 Acacia Ave in the village of Rockcliffe Park in Ottawa. Purchased in 1950 by a private trust, Stornoway has been owned by the Government of Canada since 1970 and managed by the National Capital Commission since 1986.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/d2b6590d-341d-4404-9720-e10d3b91116b.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/d2b6590d-341d-4404-9720-e10d3b91116b.jpg

Article
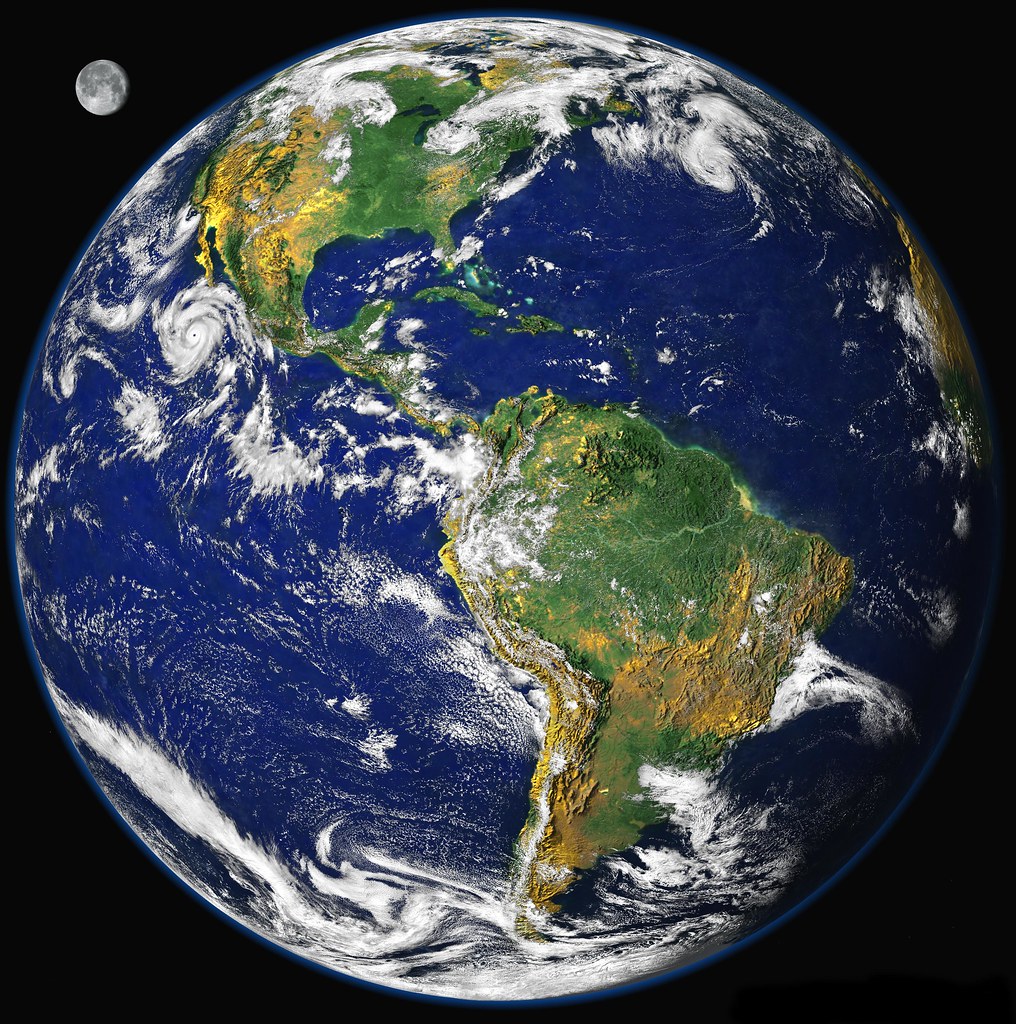
Sustainability is the ability of the biosphere, or of a certain resource or practice, to persist in a state of balance over the long term. The concept of sustainability also includes things humans can do to preserve such a balance. Sustainable development, for instance, pairs such actions with growth. It aims to meet the needs of the present while ensuring that future people will be able to meet their needs.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/new_article_images/Sustainability/Planet_earth.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/new_article_images/Sustainability/Planet_earth.jpg
Article
One of the earliest signs of authority (the right to enforce obedience) was probably a wooden club, in which symbolism grew directly out of practical application: the humble club became both an instrument by which power was exercised and (consequently) a symbol of authority.
"https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9

Macleans
The birth of his first child can change the way a man looks at things. Stephen Harper had always been a hardline ideological conservative, not given to bending.This article was originally published in Maclean's Magazine on September 29, 2003
"https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9

Editorial
The following article is an editorial written by The Canadian Encyclopedia staff. Editorials are not usually updated. On 15 February 1965, at hundreds of ceremonies across the country and around the world, the red and white Maple Leaf Flag was raised for the first time. In Ottawa, 10,000 people gathered on a chilly, snow-covered Parliament Hill. At precisely noon, the guns on nearby Nepean Point sounded as the sun broke through the clouds. An RCMP constable, 26-year-old Joseph Secours, hoisted the National Flag of Canada to the top of a specially-erected white staff. A sudden breeze snapped it to attention.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/59917f0c-b633-43e2-bb85-3d0ded55dc95.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/59917f0c-b633-43e2-bb85-3d0ded55dc95.jpg

Editorial
The following article is an editorial written by The Canadian Encyclopedia staff. Editorials are not usually updated. The Baldwin–LaFontaine government of 1848 has been called the “great ministry.” In addition to establishing responsible government, it had an incomparable record of legislation. It established a public school system and finalized the founding of the University of Toronto. It set up municipal governments and pacified French-Canadian nationalism after a period of unrest. Responsible government did not transform Canada overnight into a fully developed democracy. But it was an important milestone along the road to political autonomy. Most importantly, it provided an opportunity for French Canadians to find a means for their survival through the British Constitution. The partnership and friendship between Baldwin and LaFontaine were brilliant examples of collaboration that have been all too rare in Canadian history.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/ba6bdff6-574a-4697-ac95-afdcc5ddfcc9.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/ba6bdff6-574a-4697-ac95-afdcc5ddfcc9.jpg
